Dallas Plastics: Your Partner in Print-Ready Films
At Dallas Plastics, we understand the importance of printability when it comes to blown films used in various industries. That’s why we offer specialized printing treatments that enhance the printability of our films. Whether you’re looking to display vibrant graphics or detailed information, our treated films provide the perfect foundation for high-quality printing.
We work closely with our customers to ensure their specific needs are met, enabling seamless printing processes for converters and end-users alike. With our state-of-the-art technology and expertise, you can be confident that the films you receive are ready for print, ensuring crisp and clean results every time.
As you continue exploring this blog, you’ll find valuable insights and tips about printing on films. From understanding printing techniques to material options for printing, we’ve got you covered. Whether you’re a seasoned professional or new to film printing, this blog will guide you through the intricacies of achieving optimal print quality on flexible films.
In today’s competitive market, the demand for high-quality printed plastic films is rapidly increasing. Whether it’s for packaging, labeling, or product displays, the ability to master printing on plastic film is crucial for manufacturers, designers, and engineers. By unraveling the nuances of different printing techniques and material choices, you can unlock new opportunities to enhance efficiency, reduce costs, and improve the quality of your final products.
This comprehensive guide aims to educate professionals in the printing and packaging industries about the diverse techniques available for printing on plastic film and sheets. By exploring the benefits and limitations of each method and material, you will be equipped to make informed decisions tailored to your specific projects.
Printing on Plastic Films and Sheets
Plastic films and sheets serve as versatile substrates across various industries. They are used in packaging, advertising, labeling, and numerous other applications where durability and flexibility are paramount. Printing on plastic film allows for customization, branding, and the addition of vital information such as instructions or safety warnings.
Key Considerations When Printing on Plastics
- Surface Properties: Plastics have unique surface energies that affect ink adhesion. Pre-treatment processes like corona treatment are often necessary to improve printability.
- Ink Compatibility: Choosing inks compatible with the plastic material is critical to ensure durability and prevent smudging or fading.
- Environmental Factors: Exposure to UV light, temperature variations, and chemicals can affect the longevity of the print. Materials and inks should be chosen based on the end-use environment.
- Regulatory Compliance: Especially in food, medical, and pharmaceutical industries, materials and inks must comply with specific regulations and standards.
Common Printing Techniques for Plastic Films
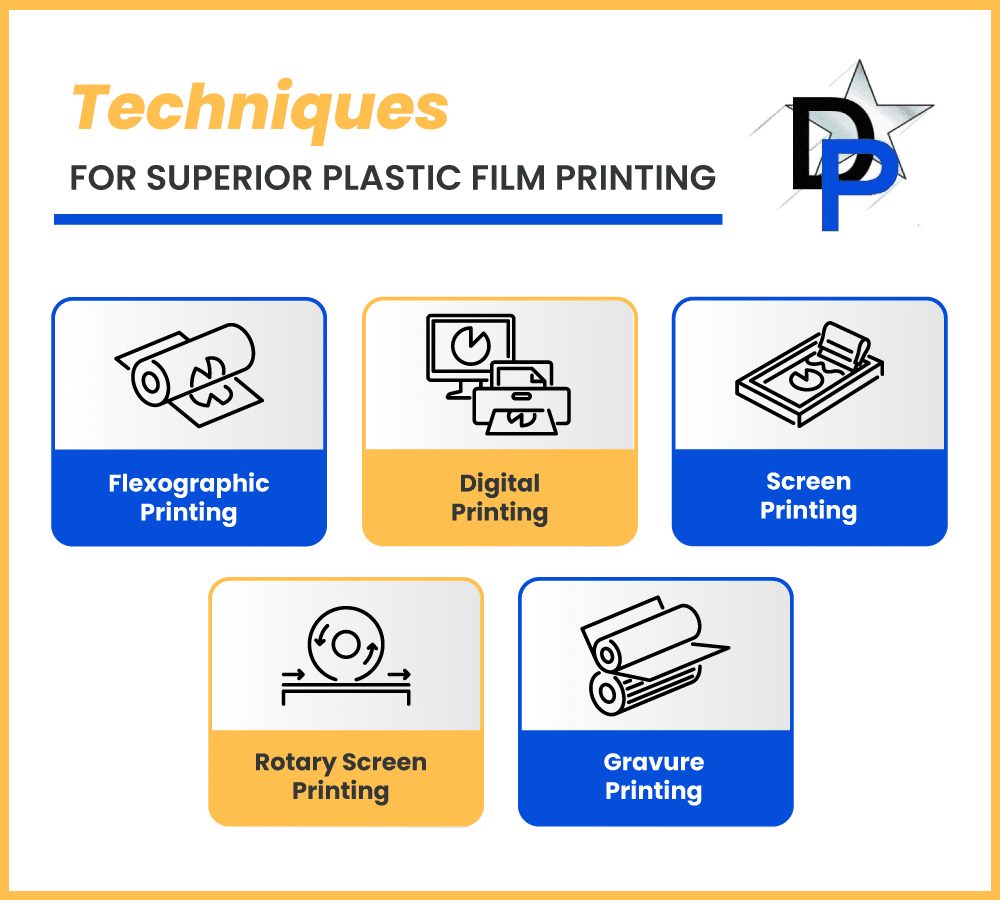
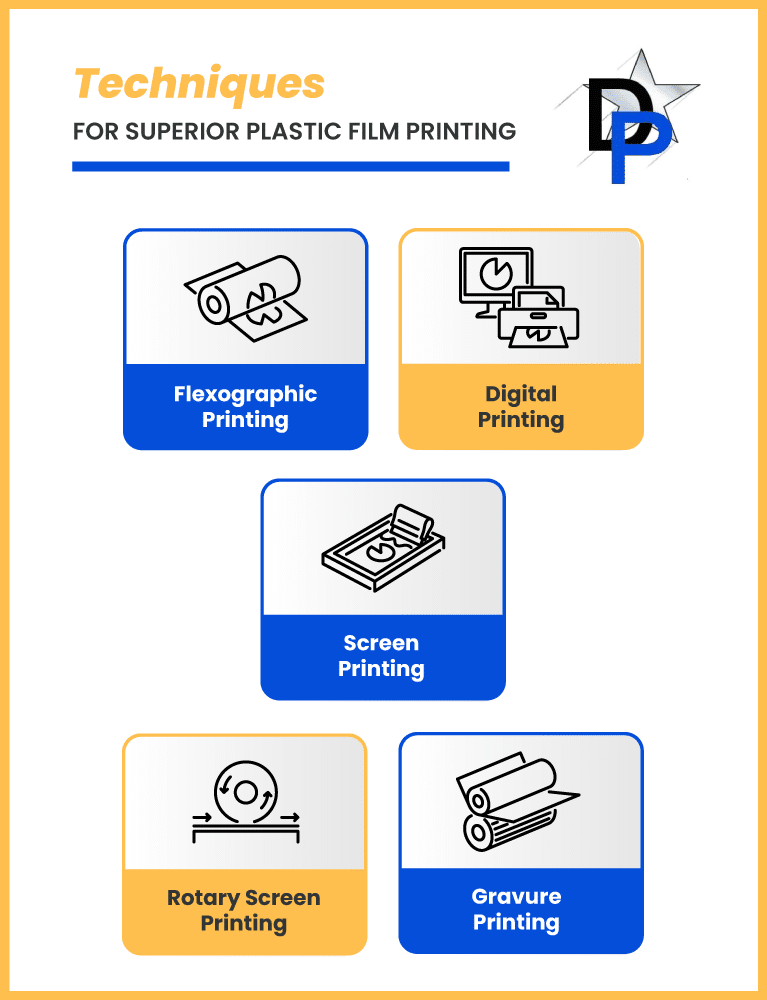
When exploring the landscape of printing on plastic films, several techniques stand out due to their distinctive advantages and applications.
Flexographic Printing
Flexographic printing, often referred to as flexo printing, is a technique known for its versatility and widespread use in producing high-volume packaging materials like bags on rolls, shrink films, and polyethylene sheeting. This method involves the transfer of ink from rollers to raised areas on flexible relief plates, which are then pressed onto the plastic film.
One of the major advantages of flexographic printing is its high-speed production, making it particularly suited for long runs. It is capable of printing on a wide array of substrates, enhancing its utility in various applications. The quick-drying inks associated with flexographic printing further improve productivity. However, the technique comes with higher initial setup costs due to the creation of plates. Additionally, it may not be as suitable for intricate, high-resolution images as other printing methods, making it more favorable for straightforward designs.
Digital Printing
Digital printing has brought significant transformations in the realm of printing on plastic film, primarily due to its flexibility and customization capabilities. It utilizes inkjet printers to directly transfer digital images onto the plastic substrate, eliminating the need for plates. This method excels in producing high-quality image reproductions with vibrant colors, making it ideal for short runs and personalized prints. The minimal setup time and costs are notable benefits for projects requiring immediate turnaround. Nonetheless, digital printing faces limitations in terms of production speed for large volumes, and the per-unit cost can be higher compared to traditional methods for extensive batches.
Screen Printing
Screen printing, also known as serigraphy, is characterized by its ability to apply thick ink deposits, resulting in vivid colors. It employs a mesh screen to push ink onto the substrate through a stencil that defines the image. Screen printing is highly advantageous for projects requiring durable prints with excellent opacity, making it suitable for rigid plastics, signage, and promotional items. Its versatility allows printing on a variety of substrates and shapes, yet it is a slower process that does not lend itself to high-volume production. Additionally, the method offers limited detail resolution compared to digital alternatives.
Rotary Screen Printing
Rotary screen printing merges the principles of conventional screen printing with the efficiencies of continuous production. This process uses a cylindrical screen that rotates to allow for the consistent application of images on plastic films, making it well-suited for high-volume production runs. Despite its higher setup costs and limited flexibility in design changes compared to digital printing, rotary screen printing maintains consistent print quality throughout extended print runs.
Gravure Printing
Gravure printing stands out as an intaglio process where the image is engraved onto a cylinder, making it especially effective for high-quality, high-volume printing on plastic film. It is commonly utilized in producing packaging, wallpapers, and gift wraps. This method achieves superior image quality, capturing fine detail and gradients due to the ink being drawn from engraved cells onto the plastic film. While gravure printing ensures highly durable cylinders for long production runs, it is not cost-effective for shorter runs due to the significant initial cost associated with engraving cylinders.
Benefits and Limitations of Each Printing Technique
Understanding the strengths and limitations of each printing technique is crucial in selecting the most efficient method for your project.
Flexographic Printing
Benefits: Flexographic printing is renowned for its high adaptability across multiple substrates, making it a popular choice for large-scale packaging operations. It is particularly cost-effective for substantial volumes due to its high-speed output, effectively reducing production costs in long-run projects.
Limitations: The quality of flexographic printing is generally good, especially for straightforward designs, but it falls short when it comes to producing intricate high-resolution images. This technique is highly scalable and excels in scenarios where long runs are required, such as in the production of bag rolls or shrink films.
Digital Printing
Advantages: Digital printing has revolutionized the printing sector with its unmatched flexibility and ability to cater to highly customizable projects. By using inkjet printers to directly apply images onto plastic substrates, digital printing negates the need for expensive plates, thus minimizing setup time and costs. This technique stands out for producing excellent image resolution with vivid colors, and it’s particularly beneficial for short-run, personalized jobs.
Disadvantages: For extensive batches, the per-unit cost can be more expensive, and its speed lags when compared to traditional methods in larger volumes. Despite these limitations, digital printing remains ideal for small to medium runs that demand prompt turnaround times.
Screen Printing
Benefits: Screen printing, also referred to as serigraphy, is preferred for its superior opacity and dense ink application, resulting in vibrant prints. It utilizes a mesh screen and stencil to transfer thick layers of ink onto the substrate, proving advantageous for projects that require durable prints. This technique shines when applied to rigid plastics, signage, and promotional items, demonstrating its versatility across a range of shapes and materials.
Limitations: While screen printing is adaptable to numerous substrates, it tends to be a slower process that doesn’t cater well to high-volume production. Furthermore, the resolution of fine details is limited when compared to digital alternatives.
Rotary Screen Printing
Advantages: Combining aspects of traditional screen printing with the advantages of continuous operation, rotary screen printing utilizes rotating cylindrical screens to produce consistent images on plastic films. It is exceptionally well-suited for high-volume runs, maintaining a steady quality throughout extended production periods.
Disadvantages: The initial setup costs are significantly higher, and there is less flexibility for design changes compared to digital printing. This method may not be suitable for projects where frequent design changes are necessary.
Gravure Printing
Benefits: Gravure printing is uniquely poised for high-quality and high-volume printing tasks, achieving exceptional image detail and gradient transitions. This intaglio method employs engraved cylinders to transfer ink to the film, frequently used in creating packaging, wallpapers, and gift wraps. The durability of the gravure cylinders is a key advantage, as they can withstand long production runs.
Limitations: Despite these merits, the high upfront costs for engraving make it less viable for shorter runs or where frequent design changes are necessary.
Material Options for Printing on Plastic Film
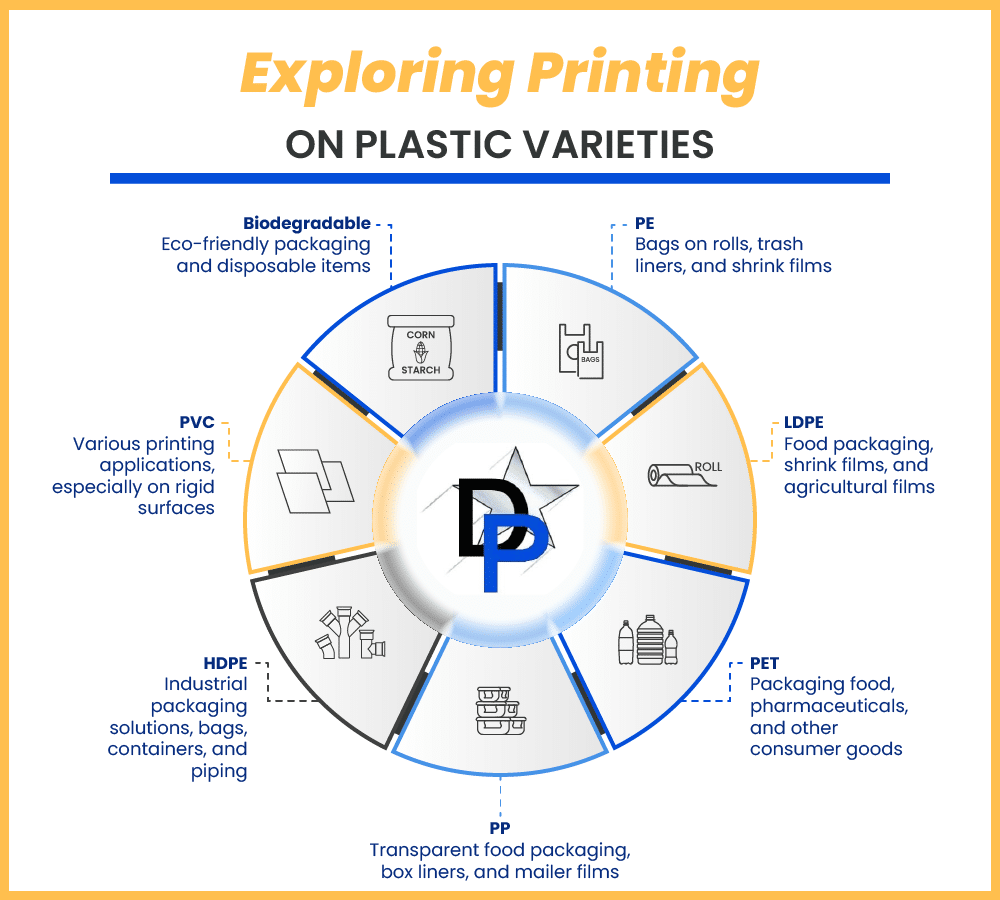
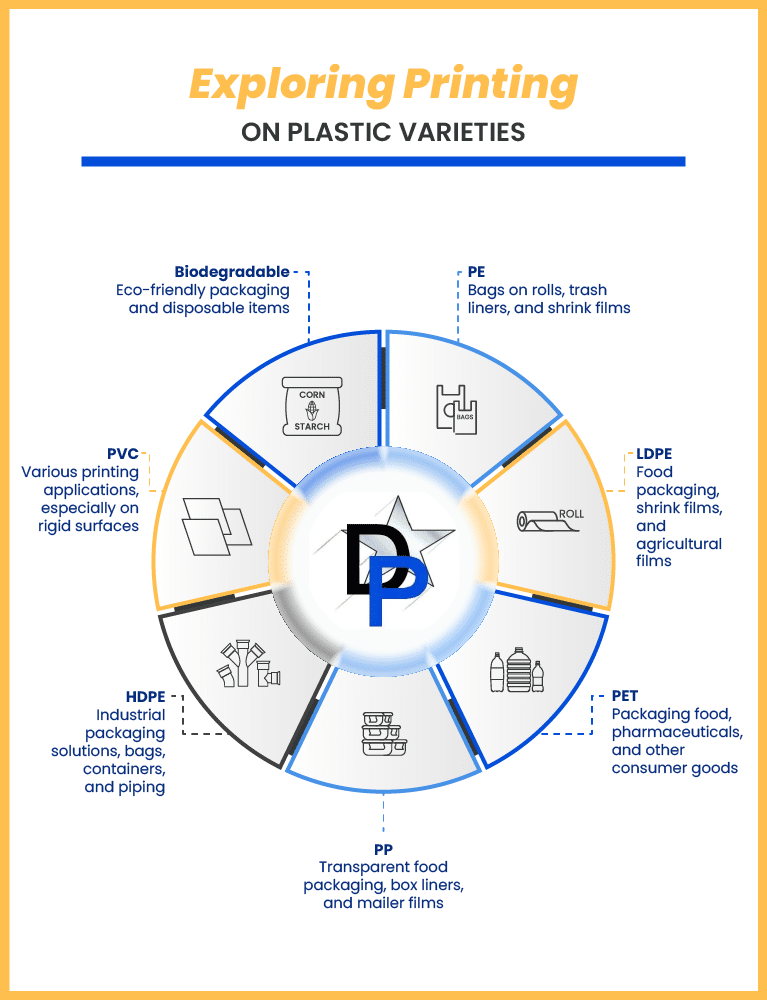
Choosing the right type of plastic material is as crucial as selecting the most suitable printing technique. Different plastic films offer unique properties that can significantly impact the quality and durability of the final print.
Polyethylene (PE)
Polyethylene is the most commonly used plastic polymer due to its flexibility and excellent moisture resistance. However, it has low surface energy, which often necessitates pre-treatment to improve ink adhesion. Polyethylene is commonly applied in products such as bags on rolls, trash liners, and shrink films.
Custom polyethylene sheeting is widely used due to its adaptability. It can be customized to meet specific requirements, such as thickness, colors, and additives for enhanced properties.
Low-density Polyethylene (LDPE)
LDPE shares most of the properties of polyethylene, including flexibility and moisture resistance. LDPE is popular for its excellent heat sealing properties and is commonly used in packaging solutions. It also boasts good chemical resistance, with particular grades offering excellent low-temperature toughness and is often used for shrink films, food packaging, and agricultural films.
High-density Polyethylene (HDPE)
HDPE is known for its stiffness and strength, making it popular for industrial packaging solutions. It is also resistant to chemicals and moisture, making it suitable for more demanding environments. It is also a popular choice for plastic bags, containers, and piping due to its excellent chemical resistance.
Polypropylene (PP)
Polypropylene is notable for its higher melting point and stiffness when compared to polyethylene, along with excellent clarity and fatigue resistance. It readily accepts inks after surface treatment, making it especially ideal for printing on transparent packaging solutions for food packaging, box liners, and mailer films.
Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET)
PET is recognized for its high strength, thermal stability, and excellent dimensional stability. Its superior clarity enhances print vibrancy, and it offers good adhesion properties with suitable inks, which is advantageous for high-quality prints. PET is frequently used for packaging food, pharmaceuticals, and other consumer goods.
Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC)
PVC comes in both rigid and flexible forms, offering good chemical resistance. It easily accepts inks, often bypassing the need for extensive pre-treatment, which makes it a favored choice for printing applications. PVC is also well-suited for printing on rigid plastic substrates due to its durability and chemical resistance.
Biodegradable Plastics
Increasingly popular for eco-friendly packaging solutions, biodegradable plastics are derived from renewable resources like corn starch. They are designed to decompose under specific conditions, and special inks may be required to maintain their biodegradability. Their surface properties can differ from traditional plastics, potentially affecting the print’s quality. Biodegradable plastics are frequently used in eco-friendly packaging, agricultural films, and disposable items.
Each of these materials offers distinct benefits and challenges, making the selection of the right film essential to ensuring successful printing outcomes.
Suitability of Materials for Various Applications
Choosing the right material for printing on plastic films is essential for ensuring the final product meets the specific requirements of its intended application. Here, we explore how different materials align with various industry needs, focusing on their properties and suitability for printing.
Food Packaging
For food packaging applications, materials like Polypropylene (PP) and Polyethylene (PE) dominate due to their excellent clarity, barrier properties, and compliance with stringent food safety regulations. Flexographic and gravure printing techniques are often employed to achieve high-quality graphics, ensuring that packaging is both functional and visually appealing. The transparency of PP, for example, makes it ideal for clear packaging solutions, while PE offers excellent moisture barriers crucial for preserving food quality.
Medical Supplies
In the realm of medical supplies, materials such as Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) and medical-grade Polyethylene (PE) are preferred due to their sterility, biocompatibility, and clarity. These properties are critical for applications where visibility of the contained product is necessary. Digital printing stands out for its ability to print variable data, such as batch numbers and expiration dates, directly on plastic films, ensuring compliance with industry standards.
Industrial Applications
Industrial applications often require materials that boast durability and chemical resistance. High-density Polyethylene (HDPE) and Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) are commonly used in these settings due to their robustness and ability to withstand harsh environments. Screen printing is frequently utilized for its capability to produce durable and robust markings on plastic films, ensuring longevity in demanding applications.
Eco-Friendly Products
As environmental concerns rise, biodegradable plastics have gained traction for eco-friendly applications. Derived from renewable resources such as corn starch, these materials are designed to decompose under certain conditions, aligning with sustainability goals. Specialized inks and processes are necessary to maintain the biodegradability of printed materials. These eco-friendly plastics are increasingly used in packaging, agricultural films, and disposable items, offering a greener alternative that meets consumer demand for sustainable products.
By understanding the compatibility of these materials with specific applications, manufacturers can ensure that the printed plastic films not only meet the technical demands but also align with industry standards and consumer expectations.
Request a Quote
How to Choose the Right Printing Technique and Material
Choosing the right printing technique and material is a crucial step that involves analyzing several critical factors relevant to your project’s specific requirements. This involves balancing the intricacies of volume needs, quality expectations, budget constraints, and the intended application of the final product.
Volume
When determining the volume, it is essential to align your technique choice with production size requirements. For high-volume production runs, methods like flexographic or gravure printing are advantageous due to their efficiency and cost-effectiveness. Flexography is particularly suited for large-scale projects such as packaging where the design is relatively straightforward. Conversely, digital printing offers greater flexibility and is a cost-effective solution for short-run projects or prototypes, allowing for customization without significant setup costs.
Quality Requirements
Quality requirements should guide the selection towards the most suitable printing technique. If the project involves detailed images and vibrant colors, gravure or digital printing techniques are preferable. Gravure printing is ideal for producing high-resolution images with fine details, which is often needed in packaging for high-end consumer goods. On the other hand, digital printing excels in producing sharp, colorful graphics, particularly when personalization or variable data is crucial.
Cost Constraints
Cost constraints are a practical consideration, where the balance between initial setup costs and per-unit costs must be evaluated. High upfront costs associated with methods like gravure printing are justified for long-term projects due to its efficient production and superior results over time. In contrast, for smaller projects or those requiring rapid turnaround times, digital printing offers lower setup costs even though the per-unit cost can be higher.
Application and End-Use Environment
The intended application and environmental exposure further influence the choice of materials and inks. Materials must align with regulatory compliance, especially in sensitive sectors such as food or medical applications. For instance, when printing on plastic films for food packaging, options like Polypropylene (PP) or Polyethylene (PE) are frequently chosen for their clarity and moisture-resistant properties. Ink selection should also account for resilience against UV light, temperature fluctuations, and chemical exposure to maintain print longevity.
Collaborating with industry professionals can offer valuable insights into making informed decisions. With their expertise, they can guide you towards the most suitable materials and techniques that align with your project’s specific needs. Additionally, they can leverage cutting-edge technologies and processes to ensure optimal outcomes that meet industry standards and regulations.

Partnering with Dallas Plastics for Your Film Selection Needs
Determining the right plastic film for a printing project is critical to achieving the desired outcome. At Dallas Plastics, we excel in guiding you through the complexities of film selection to ensure that your project meets industry standards and customer expectations. Whether you’re dealing with food packaging, medical supplies, or eco-friendly products, our expertise helps you navigate material options that align with your specific needs and printing requirements.
Unlock the potential of your plastic film printing endeavors by collaborating with our experienced team. At Dallas Plastics, we bring over 35 years of industry leadership and a commitment to innovation, making us your trusted partner in selecting the optimal film that best suits your vision and objectives. Reach out to Dallas Plastics today to take the first step in transforming your projects with the right materials.




