Polyethylene (PE) film is a cornerstone in numerous industries, including packaging, agriculture, medical supplies, and consumer goods. Its versatility, durability, and cost-effectiveness make it indispensable for products like food packaging, shrink wraps, medical packaging films, and agricultural mulch films. However, the sustainability of polyethylene film is a growing concern due to escalating plastic pollution and climate change.
The focus on polyethylene film sustainability has become critical for environmentalists, industry professionals, and policymakers. Balancing the functional benefits of PE films with their environmental impacts is essential for sustainable ecological practices.
This comprehensive analysis explores the environmental footprint of PE films, technological advancements promoting sustainability, improvements in recycling capabilities, industry innovations, regulatory influences, and future trends shaping the sustainability landscape of PE films. By understanding these factors, stakeholders can make informed decisions to advance sustainability in their respective fields.
The Environmental Impact of PE Film
Production Processes and Carbon Footprint
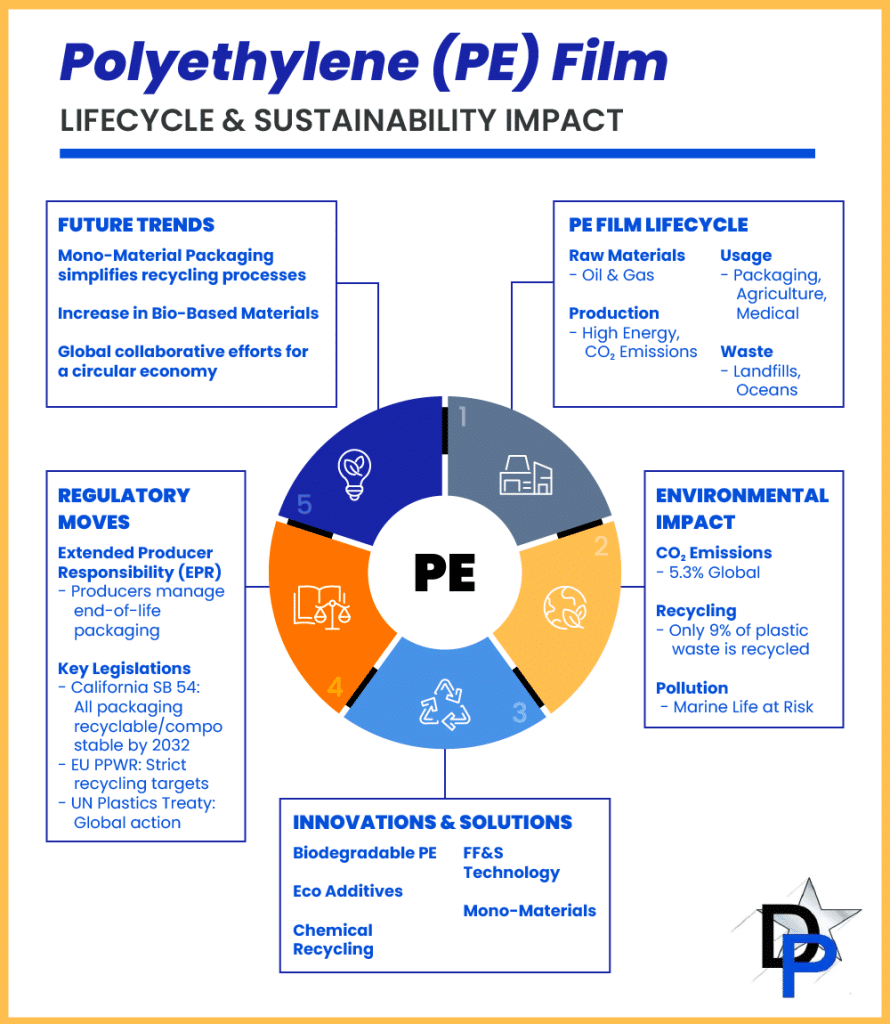
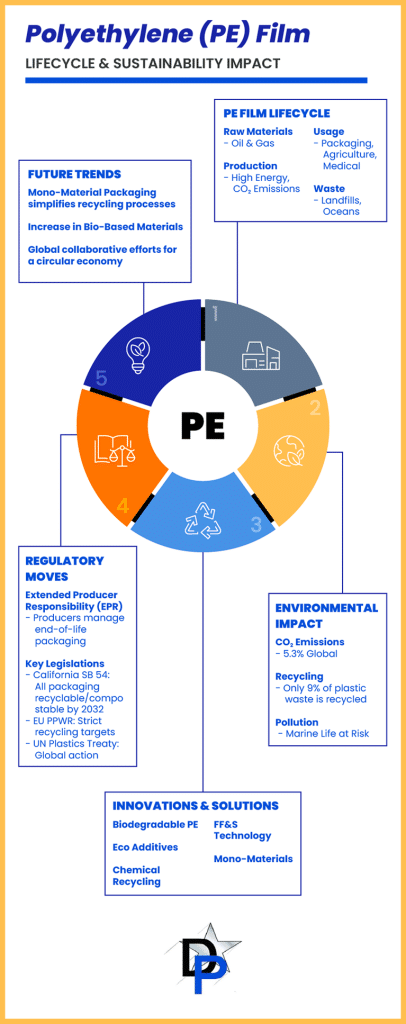
Polyethylene film production, while offering numerous functional benefits, is an energy-dependent process primarily powered by fossil fuels. Each kilogram of polyethylene generates between 1.7 and 3.5 kg of CO2 equivalents, highlighting the potential for innovation in reducing emissions. For context, around 2.24 billion metric tons of CO2 equivalents were attributed to virgin plastic production in 2019, representing about 5.3% of global emissions. This presents an opportunity to explore and adopt cleaner production technologies and energy sources to lower the carbon footprint.
Environmental Persistence and Pollution
The durability of PE films is a significant advantage, ensuring the longevity and reliability of products across multiple industries. However, this durability means the films can remain in the environment for extended periods, collecting in landfills and occasionally in natural settings. Every day, a significant amount of plastic waste ends up in our oceans and waterways. Improving waste management practices and exploring biodegradable alternatives can help manage PE film’s accumulation and support healthier ecosystems.
Economic and Ecological Aspects
While plastic pollution poses challenges, it also offers a chance to drive innovation in waste reduction and resource recovery. The potential economic benefits are substantial, as reducing marine plastic pollution could protect industries like tourism and fisheries while preserving biodiversity. The financial impact of marine plastics underscores the importance of sustainable practices that can yield long-term ecological and economic dividends. By fostering collaboration across sectors, stakeholders can create comprehensive strategies that support sustainable growth and environmental stewardship.
Technological Advancements in Sustainable PE Film
Development of Biodegradable and Compostable Alternatives
Innovations in materials science have propelled the development of biodegradable and compostable alternatives to traditional PE films. These materials break down naturally in the environment, reducing the accumulation of plastics in landfills and oceans. While there is still work to be done to optimize these materials, they offer a promising pathway to sustainable PE films.
Introduction of Eco-Friendly Additives
The incorporation of eco-friendly additives in PE film production can enhance biodegradability. These additives promote the breakdown of polymers when exposed to specific environmental conditions, such as increased microbial activity in landfills. While not a complete solution, they represent a step toward mitigating the environmental impact of PE films.
Precision Agriculture and Reduced Material Usage
Technological advancements in precision agriculture and vertical farming contribute indirectly to polyethylene film sustainability. By optimizing crop production, the demand for agricultural films like mulch films can be reduced or managed more efficiently. This approach minimizes the utilization of PE films in agriculture, thereby decreasing overall environmental impact. Additionally, precision techniques ensure that materials are used more effectively, reducing waste.
Enhancing Recycling Capabilities of PE Film
Current Recycling Practices and Challenges
Recycling PE film poses significant challenges due to its thin, flexible nature, which often interferes with recycling machinery designed for rigid plastics. Additionally, contamination with food residues and the presence of multi-layered films further complicate the recycling process. As a result, only 9% of plastic waste is currently recycled globally, highlighting the need for better recycling capabilities.
Innovations in Recycling Technology
Advancements in recycling technologies offer promising solutions to these challenges. Chemical recycling processes can break down PE films into their monomers, allowing for the production of new plastics without degrading material properties. This technology not only supports a circular economy but also reduces the environmental impact of PE film production.
Improving Recycling Infrastructure
Improving recycling infrastructure is vital for managing PE film waste more effectively. By investing in technologies like optical sorters and wash lines, recycling facilities can better sort and clean PE film waste for processing. Additionally, investing in collection and sorting infrastructure can improve the quality and quantity of recycled material, supporting a circular economy for PE films.
Certification Programs and Consumer Participation
Certification programs generally play a role in enhancing the credibility of recycling claims and encouraging consumer participation. By providing clear labeling and accepting specific types of PE films for recycling, these programs aim to increase recycling rates. Educating consumers on proper disposal methods is crucial for reducing contamination and enhancing the effectiveness of recycling streams.
Industry Innovations Facilitating Sustainability
Adoption of Form, Fill, and Seal (FF&S) Technology
The adoption of Form, Fill, and Seal (FF&S) technology streamlines packaging processes, reducing material usage and waste. By forming the packaging material around the product during filling, this technology minimizes excess material, potentially contributing to polyethylene film sustainability. Dallas Plastics specializes in FF&S technologies, offering high-quality PE films optimized for this application.
Use of Recycled Materials in Manufacturing
Incorporating recycled materials in the production of PE films can significantly reduce the environmental impact of the industry. By replacing virgin plastic with recycled materials, companies can reduce greenhouse gas emissions, energy consumption, and waste, while also supporting the circular economy.
Multi-Layer Coextrusion and Mono-Material Films
Advancements in multi-layer coextrusion techniques allow for the production of films with enhanced properties while using less material. There is a shift towards mono-material films that simplify the recycling process, maintaining functionality without compromising sustainability. This innovation supports the creation of more efficient and eco-friendly packaging solutions.
Regulatory Landscape and Its Impact on PE Film Sustainability
Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) Legislation
Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) legislation policies are gaining global traction, shifting the responsibility of waste management from consumers and governments to producers. In the United States, states like California have introduced EPR bills requiring companies to redesign packaging and source alternative materials to meet recyclability and sustainability goals.
California’s SB 54 and Its Implications
California’s SB 54 mandates that all single-use packaging be recyclable or compostable by 2032, with a significant reduction of plastic packaging. Additionally, it requires that producers adhere to strict recycling rate goals and end-of-life management, significantly influencing packaging design and material sourcing, compelling companies to innovate and adopt sustainable practices.
International Regulatory Efforts
Globally, the European Union’s Packaging and Packaging Waste Regulation (PPWR) sets ambitious recycling targets and bans on certain single-use plastics (Dentons). Furthermore, the United Nations’ Plastics Treaty, involving 175 nations, represents a concerted effort to reduce global plastic pollution through collaborative regulation and international cooperation.
Overcoming Challenges in Transitioning to Sustainable PE Films
Economic Barriers and Cost Implications
Transitioning to sustainable PE films involves costs for manufacturers, including investments in new technologies, materials, and production processes. However, economies of scale, government incentives, and increasing consumer demand for sustainable products can mitigate these costs over time. Strategic investments and partnerships can further support this transition.
Addressing Consumer Behavior and Awareness
Consumer habits play a crucial role in the success of sustainable initiatives. Although surveys indicate that consumers are increasingly aware of the importance of sustainable packaging, actual purchasing behaviors often lag due to convenience and price sensitivity. Educating consumers about the environmental benefits and promoting easy-to-recycle packaging can bridge this gap.
Technical Challenges in Material Performance
Maintaining the desirable properties of PE films—such as strength, clarity, and barrier performance—while enhancing sustainability presents technical challenges. Ongoing research and development focus on creating materials that do not compromise on performance while offering environmental benefits.

Future Prospects and Trends in Sustainable Polyethylene Film
Growth in Mono-Material and Recyclable Films
The market for mono-material packaging is projected to grow significantly, reflecting a trend toward packaging solutions that are easier to recycle, supporting a circular economy. Companies are investing in research to optimize these materials for various applications.
Advancements in Bioplastics and Bio-Based Materials
The market for bioplastics and bio-based materials is expected to grow substantially, offering a biodegradable and renewable alternative to traditional plastics. These materials are increasingly being used in sustainable packaging solutions, reducing the environmental impact of PE films.
Emphasis on Sustainable Sourcing and Supply Chain Management
Companies are increasingly focusing on sustainable sourcing and ethical supply chain management. This involves reducing carbon emissions, promoting eco-friendly production practices, and ensuring fair labor practices. Sustainable sourcing and supply chain management are crucial for promoting sustainability throughout the entire lifecycle of PE films.
Collaborative Efforts and Circular Economy Initiatives
Collaborative efforts are crucial for driving sustainable practices in the polyethylene film industry. Partnerships between governments, industries, and consumers can promote innovation, improve waste management infrastructure, and create a market for sustainable products. Collaborative initiatives like The New Plastics Economy Global Commitment aim to transition to a circular economy for plastic packaging, facilitating sustainable practices across the industry.
Moving Towards Sustainable Practices in the Polyethylene Film Industry
The path towards sustainable polyethylene film is complex, involving a synergy of technological advancements, regulatory measures, industry innovation, and consumer consciousness. The integration of innovative solutions such as those provided by Dallas Plastics plays a crucial part in this journey. By specializing in Form, Fill, and Seal (FF&S) technologies, Dallas Plastics reduces material usage and waste, positioning itself as a crucial player in promoting sustainable PE films.
Dallas Plastics plays a pivotal role in the transition towards a more sustainable future for polyethylene films. By leveraging their expertise and technology, they contribute significantly to environmental responsibility and innovation within the industry. The collaborative effort to adopt sustainable practices can foster positive changes both environmentally and commercially, encouraging organizations and individuals alike to engage in initiatives that prioritize ecological integrity


